Diamond: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(→Types) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Right of Way]] | [[Category:Right of Way]] | ||
== Types == | |||
There are several types of track crossing arrangements. | |||
=== Diamond Crossing === | |||
A diamond crossing is formed when two tracks cross each other at less than 90 degree angle. | |||
=== Square Crossing === | |||
A square crossing is formed when two tracks cross each other at a right (90 degree) angle. | |||
=== Full Flange Bearing === | |||
From [https://www.rail-suppliers.com/product/full-flange-bearing-diamond/ <i>Progress Rail</i>]: | |||
: Eliminates wheel contact at the flange way intersection of the diamond. Significantly reduces impact that leads to accelerated maintenance and eventual replacement of the castings and sub-components. | |||
[[File:Progress-Rail-Full-Flange.jpg|thumb|center|500px]] | |||
== Examples == | |||
=== CIG === | |||
Ken Smith built this [[Diamond|diamond]] for the [[Comanche & Indian Gap Railroad]]. He used flat bar for all components, with the exception of the short section of steel rail as a transition between the diamond and the aluminum rail. This diamond could be adapted to Full Flange Bearing type. | |||
Here is the material list used for constructing the diamond (either [[HRS]] or [[CRS]]): | |||
* 1/2 by 1 inch flat | |||
* 1/4 by 3/4 inch flat | |||
* 1/8 by 1 inch flat | |||
* 2 by 1/8 inch flat | |||
* 1 by 1 inch angle | |||
<gallery widths=300px heights=300px perrow=2> | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.16.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.21.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.23.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.27.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.33.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.41.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.15.57.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.16.00.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.16.06.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.16.20.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-16 18.16.23.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-17 11.11.05.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-18 07.32.18.jpg | |||
File:CIGRR Diamond 2020-10-18 07.32.25.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://discoverlivesteam.com/2015/04/12/constructing-a-diamond-junction/ "Constructing a Diamond Junction", <i>DiscoverLiveSteam.com</i>] | * [https://discoverlivesteam.com/2015/04/12/constructing-a-diamond-junction/ "Constructing a Diamond Junction", <i>DiscoverLiveSteam.com</i>] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 29 May 2021
Types
There are several types of track crossing arrangements.
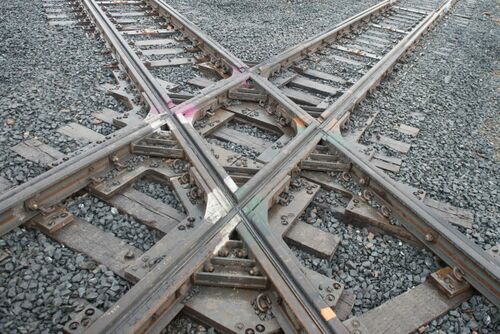
Diamond Crossing
A diamond crossing is formed when two tracks cross each other at less than 90 degree angle.
Square Crossing
A square crossing is formed when two tracks cross each other at a right (90 degree) angle.
Full Flange Bearing
From Progress Rail:
- Eliminates wheel contact at the flange way intersection of the diamond. Significantly reduces impact that leads to accelerated maintenance and eventual replacement of the castings and sub-components.
Examples
CIG
Ken Smith built this diamond for the Comanche & Indian Gap Railroad. He used flat bar for all components, with the exception of the short section of steel rail as a transition between the diamond and the aluminum rail. This diamond could be adapted to Full Flange Bearing type.
Here is the material list used for constructing the diamond (either HRS or CRS):
- 1/2 by 1 inch flat
- 1/4 by 3/4 inch flat
- 1/8 by 1 inch flat
- 2 by 1/8 inch flat
- 1 by 1 inch angle